
LFV-BIAX Servohydraulic Biaxial Planar Testing Systems
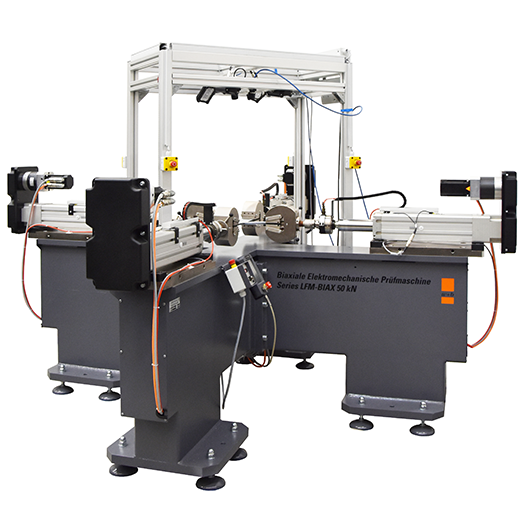
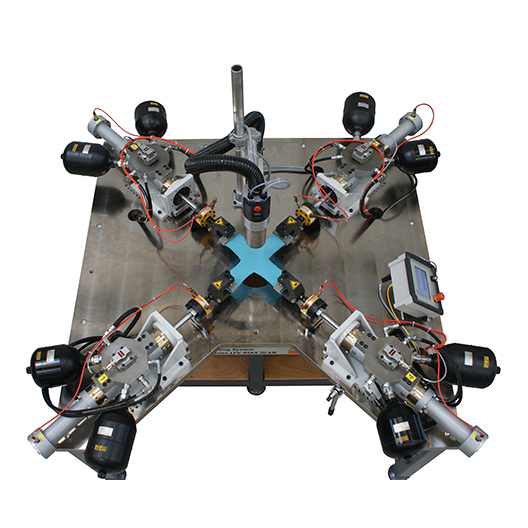
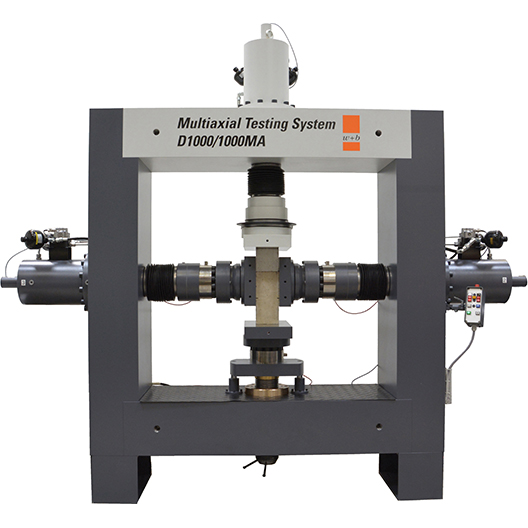
During service engineering, components are often subjected to multiaxial stresses. For biaxial testing of materials, particularly composites, metals, textiles, biomaterials and plastics w+ supplies Axial-Torsional Test System, Planar Test System as well as Triaxial Test system. For Biaxial Planar Testing the samples are typically of a cruciform shape. Biaxial system is capable of independent control of load applied to cruciform specimen trough four actuators. The cruciform specimen avoids stress concentrations and provide a uniformly stressed test section.
Load application for the cruciform can be accomplished in a robust frame supplied with separate drives (either electromechanical or servohydraulic) and separate load cells to prevent the unbalanced loading. Depending on test conditions w+b offers Biaxial Testing Systems in different configurations adapted to multiaxial testing in creep, static strength, fatigue or high speed mode in different force ranges. The available systems are with electromechanical drives or with servohydraulic actuators.
What is Planar Biaxial Testing
Planar biaxial tests apply a controlled tension-tension / compression-compression / tension-compression or the before mentioned loadings with additional torque moment state of stress and strain to specimens to help characterize anisotropic behaviour. The data produced provides inputs for constitutive modelling of materials and enables researchers to compare new advanced materials to existing or native materials. They can help assess anisotropy, nonlinear stress-strain relationship and viscoelasticity. Planar biaxial systems can be configured for static, dynamic and fatigue testing applications. The machines are specially engineered and configured
to meet specific customer specimen dimensions and test conditions. Four grips attach the test sample to the machine actuator along each of the flat specimen's four sides. The machine can be configured with two or four actuators that apply their load to the sample along two primary axes.
What is the Purpose of a Planar Biaxial Test
Planar biaxial tests determine the mechanical properties of the test sample that experiences biaxial states of stress. The stresses applied to a sample during a planar biaxial test represents the stresses the material will experience during actual service conditions, it can also be used for modelling purposes. Planar biaxial test data is superior to uniaxial test data if the material or end-product experiences stress in complex multiaxial configurations during its lifetime. Biaxial tensile strength, compressive strength, flexural strength, fracture properties and fatigue life can all be determined for a material using a planar biaxial test. Our planar biaxial test systems can perform tension-tension, tension-compression, compression-
compression and tension-shear tests.
Tests Made Possible with a Planar Biaxial Tester
Our planar biaxial testers can be configured to serve a range of test samples with different load capacity, sample sizes, and sample elongations. Test configurations may include uniaxial tests that can be performed on the same sample. To apply a bi-directional load to a material it must be formed into a thin rectangular shape, also known as cruciform, and applied loads are then configured to be perpendicular to one another. The load applied to the sample may use one or more of the following stress methods: tension, compression, flexure, shear, fracture toughness, and/or fatigue.
Types of Materials Used in Planar Biaxial Tests
The most common planar biaxial tests are performed upon soft biological tissues, fibrous soft tissues, metal plates and sheet, hard foams, hyperplastic rubber, composite laminates, thin films, fibre reinforced polymer composites, silicone elastomers, textile materials, flexible material and rigid substrates. Soft biological tissue tests are common in the biomedical industry.